Maraş became Kahramanmaraş after the War of Independence, taking the title of “Kahraman” (Hero). Kahramanmaraş also hosted many civilizations and empires, which carried on throughout the history. It is located in the foothills of Ahir Mountain and among Adıyaman, Malatya, Gaziantep, and Osmaniye. The fact that it is located on the skirts of a mountain means that the city terrain is just crinkled enough to be rough. Although areas further from the city center are generally flat, the city itself has a rugged structure. When we look at the structure of Turkey, the city is located exactly in the middle of three regions. Because of this, many seasons cycle in this city. The region is regarded as the Mediterranean and its climate is generally in accordance with the Mediterranean climate.
Afşin, Elbistan, Nurhak, Pazarcık, Türkoglu, Göksun, Andırın, and Dulkadiroğlu are some of the provinces of Kahramanmaraş. The city has a developed textile sector. Apart from this, there are many dams in Kahramanmaraş: Sır Dam, Menzelet Dam, Kartalkaya Dam, Ayvalı Dam, Guided Dam, and Adatepe Dam.
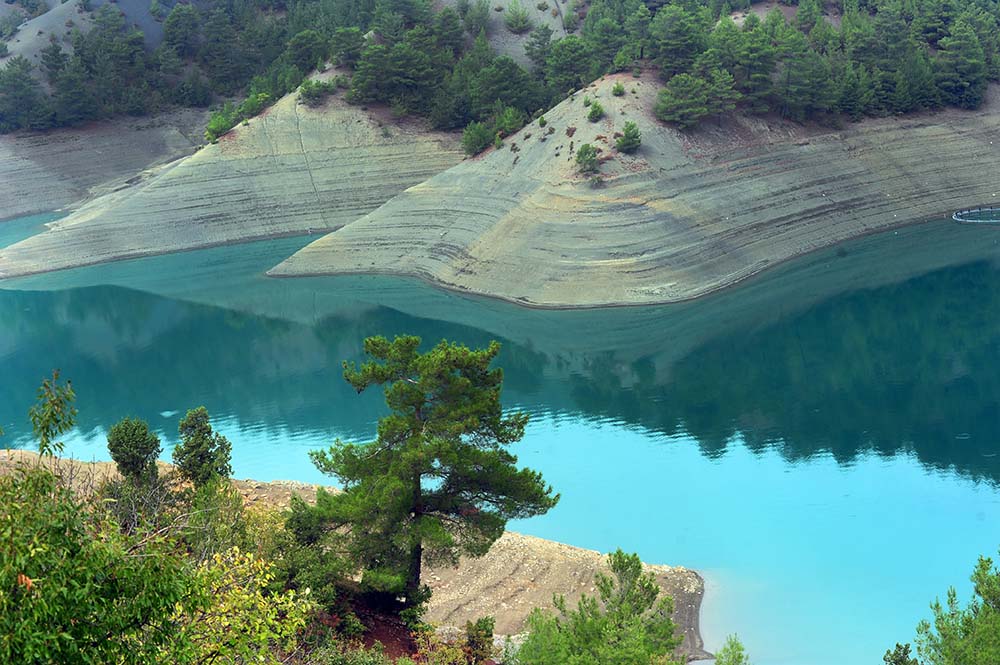

Menzelet dam lake
Alongside its natural culture and history, Kahramanmaraş is among the places that should be seen in the Mediterranean Region, in particular to spend time with its welcoming people. Historical places that can be visited in Kahramanmaraş include:
- Grand Bazaar
- Hurman Castle: The castle attracts tourists with its long history and splendid architecture, and it consist of many walls.
- Elbistan Grand Mosque
- Kahramanmaraş Museum: This building, first known as Taş Madrasa, was the first-ever museum in Kahramanmaraş.
- Kahramanmaraş Castle
- Ceyhan Bridge
- Döngel Caves
- Gumuskaya Cave: This cave, which has formed during the Paleocene period, is visited too much because it is located on the Silk road.
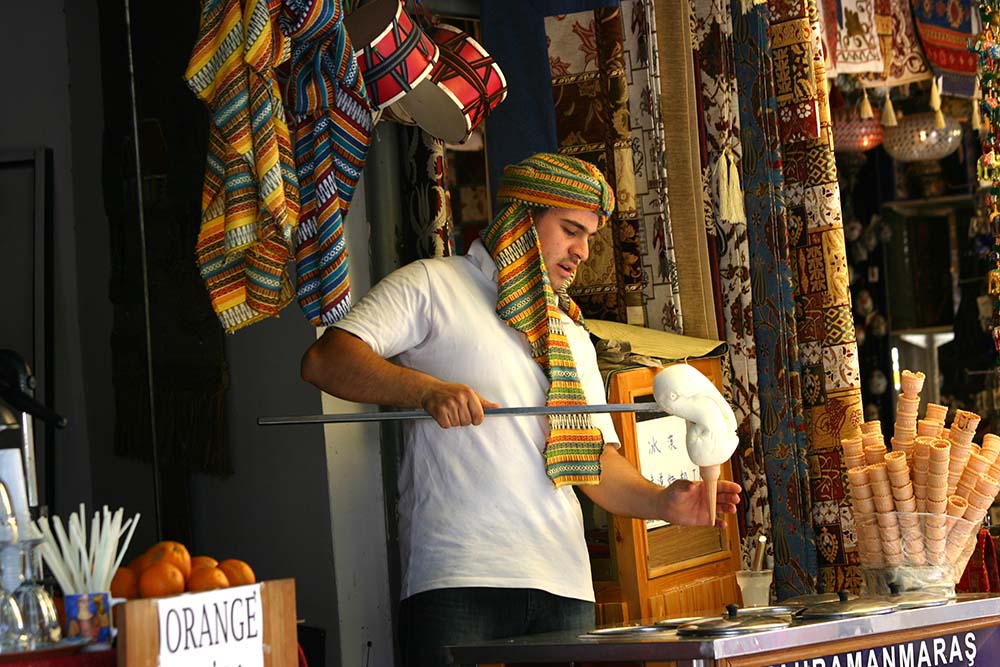

Famous ice-cream of Kahramanmaraş.
- Çorran Waterfall: This waterfall, preferred for mountain and highlands tourism, is located in an easily accessible area.
- Great Cranberry Mineral Spring
- Tekir Yesilgöz Recreation Area
- Ekinözü Mineral Spring
- Savruk Cave
- Kapıçam Nature Park
- Direkli Cave
- Döngel Cave
- Kumaşır Lake
- Bulut Deliği Caves
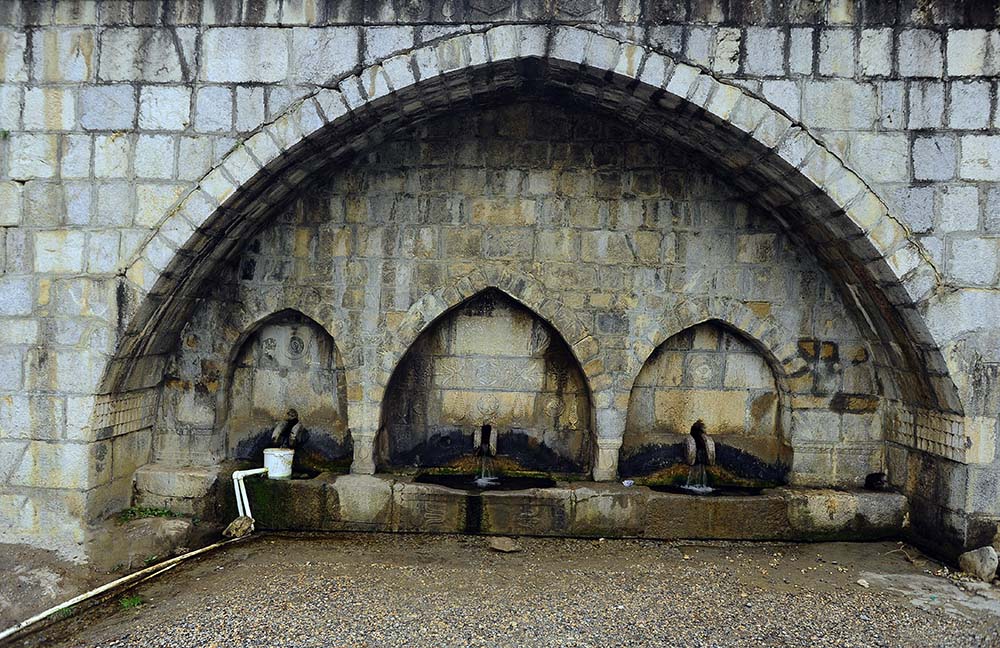
Suleymanli Antique City Fountain.
Cuisine
Kahramanmaraş’ cuisine is diversified, and offers something for everyone. The delicious smells coming from narrow streets bring entice to visitors. Many dishes, from main courses to desserts, from salads to soups, from dumplings to meatballs, are a part of Kahramanmaraş culture, including acem pilaf, Turkish soup, leğen soup, meat borek, pistachio rice, flatbread, sour carrot salad, kebab, pumpkin porridge, dövme aşı, carrot stuffing, peanut butter, ice cream, and sudjuk. The most famous of these is the strong ice cream, made of mastic and salep.
How to Get There
The city is well connected via bus network, and highways.



